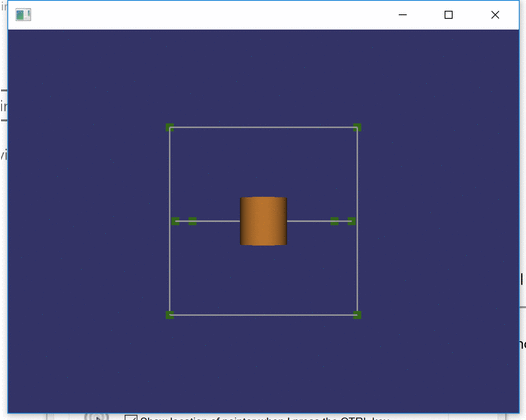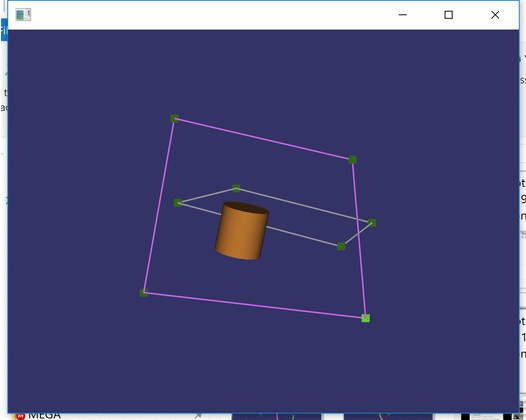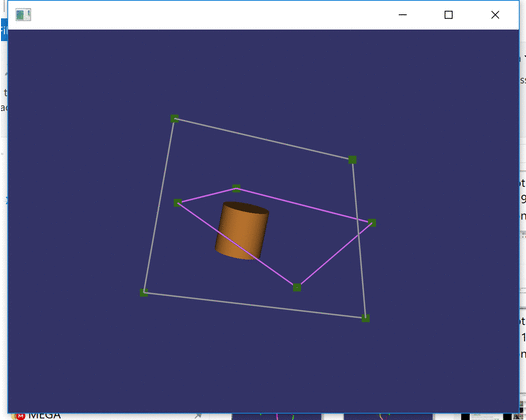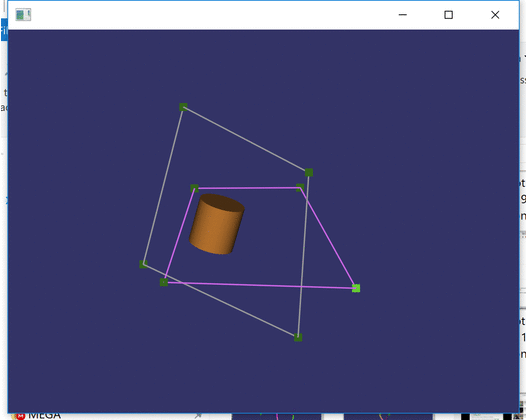
When I was building CAD-like program, one of the essential needs was different types of intersectors. The purpose was to be able to select different elements such as points, lines and drag them in a special manner, e.g., so that dragged rectangle point remains in the same plane as the rectangle.
The tiny demo program I created demonstrates how to use exactly the aforementioned intersectors. In short, I provide three types of intersectors:
This post’s main goal is to describe the created demo. All the parts of the demo are based on previous tutorials which will provide in depth details, if necessary.

Line intersection is based on finding the shortest distance between the raycast and all the line elements on the scene. For more details on how the line intersector works, feel free to check part 1 and part 2 of the corresponding tutorials.
Within the demo code, the line intersection is in action whenever you observe the wire’s color to turn magenta color.
The point intersection is based on finding the shortest distance between the raycast and all the point elements, and then finding of the distance is within a threshold. This part is heavily based on Chapter 10 of OpenSceneGraph Cookbook. In the article you can find all the necessary details on how the method works.
Within the demo code, the point intersection is in action whenever you observe the point’s color to turn bright green. That indicates the selected point is within the threshold distance from the ray casted from the camera view through the mouse position.
The virtual plane intersector is based on finding an intersection point between the ray that was cast by the mouse with a virtual plane in 3D. An example of application of such intersector could be drawing on plane in 3D. For the demo, we use it to assure the dragged point elements stay within the same plane as the rectangle. More precisely, the intersector helps to find a new position of the wire corner by finding an intersection between the mouse ray and the virtual plane of the rectangle.
Within the demo, the intersector is used whenever the mouse drags a point. In this case, it is indicated by yellow color.